Welding materials, known as the "binding agent" of the steel industry, play a vital role in downstream sectors like construction, heavy equipment manufacturing, automotive, shipbuilding, and more, significantly impacting the overall development of the manufacturing sector. However, traditional welding material factories face challenges due to low levels of automation, complex production processes, safety risks in operations, and underutilized storage space. Addressing these challenges head-on, VisionNav offers a comprehensive internal logistics automation solution tailored for the welding materials industry.
PROJECT OVERVIEW
The company is a renowned manufacturer of welding materials. The project involves multiple areas, including the finished product offloading zone, roller conveyor line, empty pallet onboarding zone, and line storage area. The client aims to enhance logistics efficiency by introducing VisionNav's advanced intralogistics automation solution.
https://youtu.be/IIBy9Ggoqf4
SOLUTION
To meet the client's requirements, VisionNav provides a solution consisting of the VNP20 balance-stacking autonomous forklift, the RCS 2.0 centralized control and dispatch system, and the inventory management system. Through the integration of the RCS 2.0 system with the client's PLC control system, the inventory management system efficiently plans storage locations. VisionNav enables the automation of processes such as finished product offloading, stacking during storage, and timely replenishment of empty pallets.
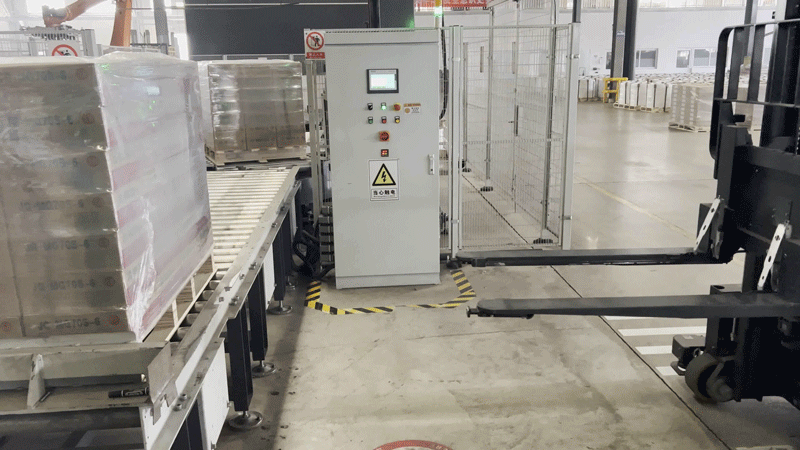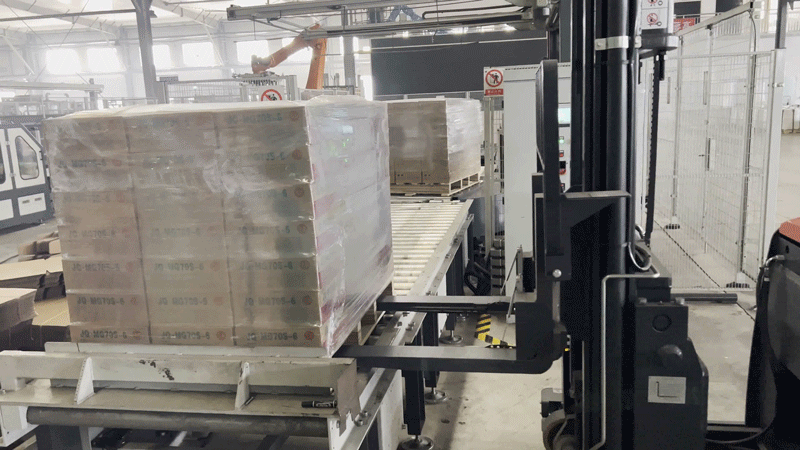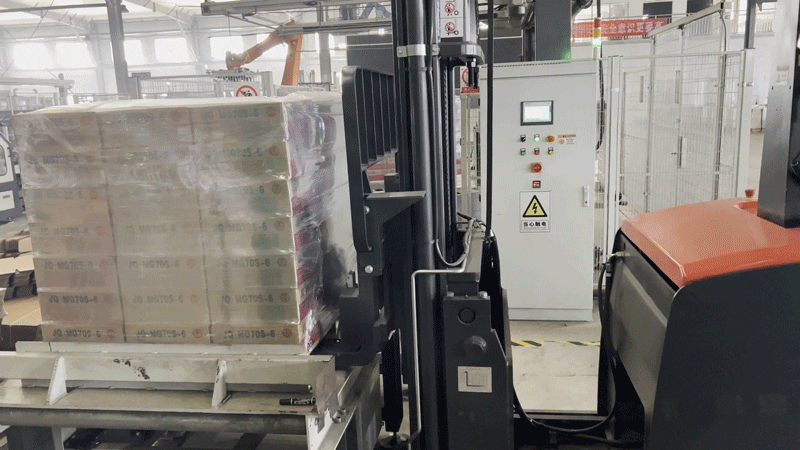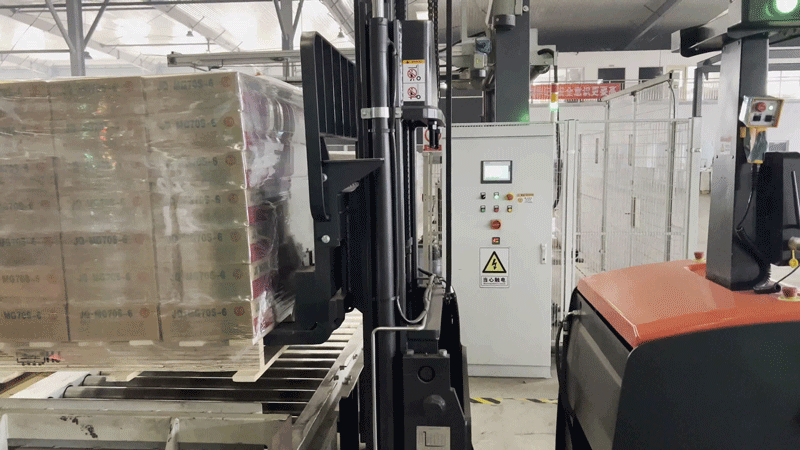
PROJECT WORKFLOW
1/ Finished Product Storage, Three-tier Stacking:
The VisionNav RCS 2.0 centralized control and dispatch system integrates with the client's conveyor line PLC control system. When the roller conveyor line delivers a stack of finished products to the offloading zone, the conveyor line sends a signal to the RSC 2.0 system through the PLC control system to indicate that the products have arrived. Based on the operational status of the autonomous forklifts on-site, the system intelligently dispatches an available VNP20 autonomous forklift to retrieve the stack of finished products from the roller conveyor line.

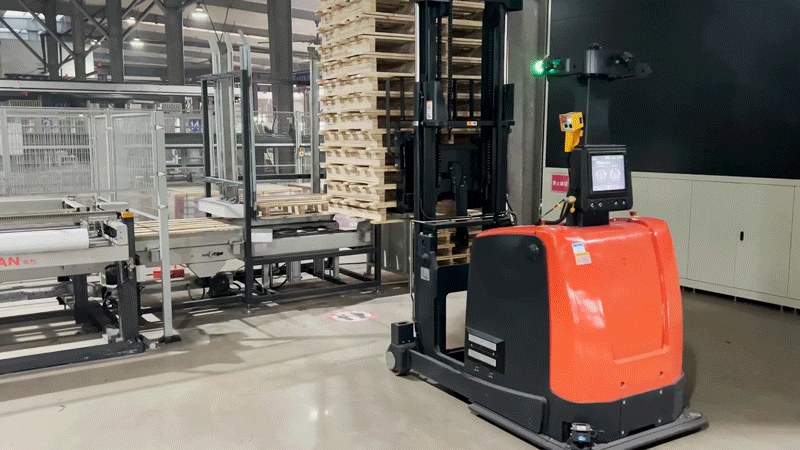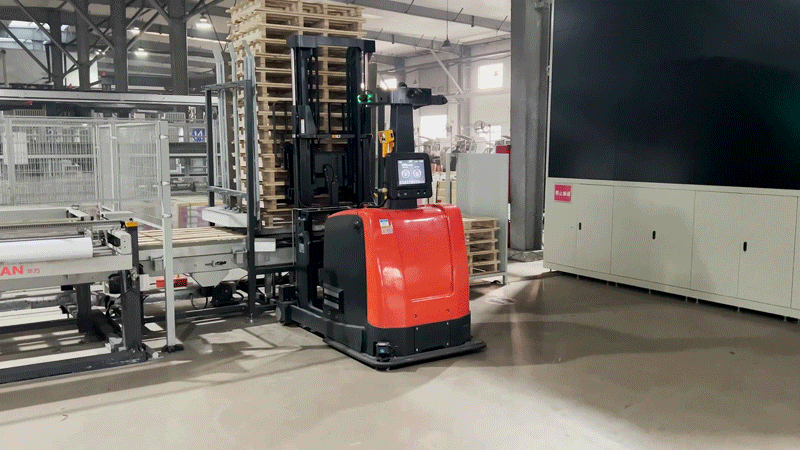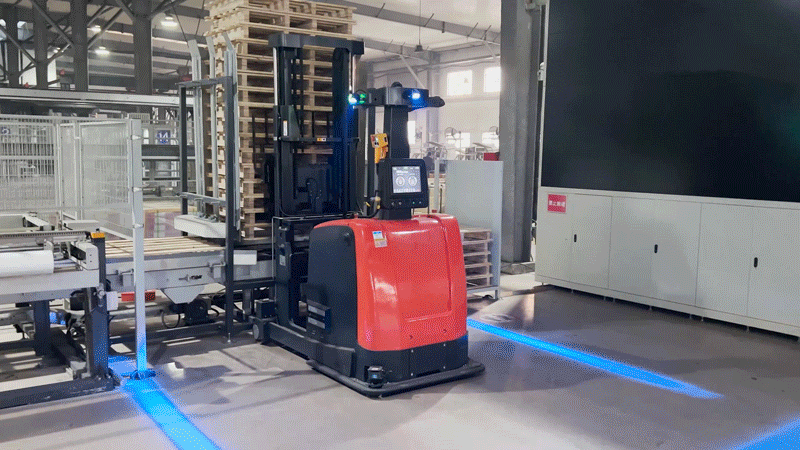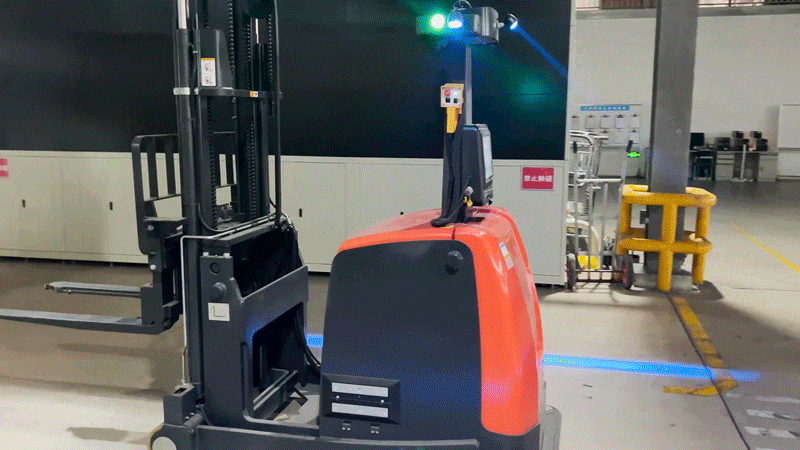
After the autonomous forklift (VNP20) retrieves the stack of finished products, it transports them to the designated location based on the storage location information provided by the inventory management system. The autonomous forklift then completes the storage process by precisely stacking the products in a three-tier configuration.
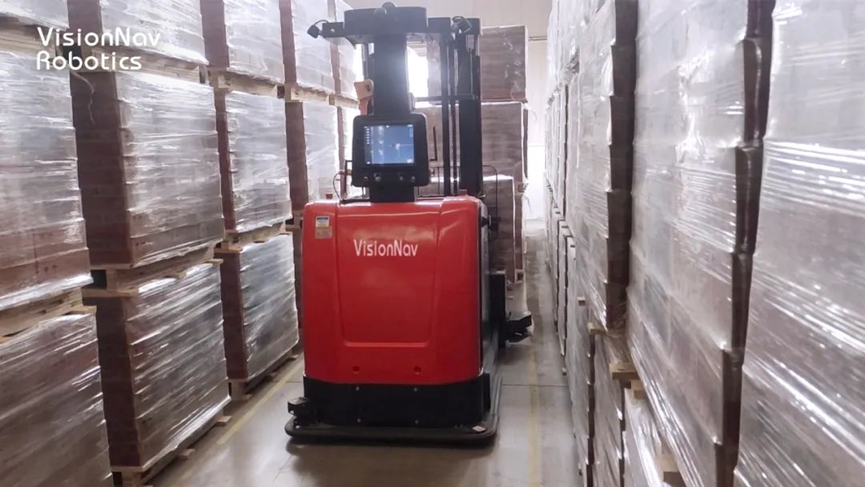

2/ Timely replenishment of empty pallets:
In the empty pallet onboarding zone, when the pallet dismantling machine detects a shortage of pallets, the PLC control system of the dismantling machine sends a signal through the RCS 2.0 dispatch system to the autonomous forklift. The system intelligently dispatches an available VNP20 autonomous forklift to the designated area for storing pallets. The forklift retrieves the pallets and transports them to the pallet onboarding zone, where it interfaces with the pallet dismantling machine. The forklift places the pallets onto the dismantling machine, ensuring timely replenishment of pallets.
PROJECT ACHIEVEMENTS
1. Timely response, efficient operations: By integrating the RCS 2.0 dispatch system with the client's system, the operational requirements are relayed to the autonomous forklifts. The autonomous forklifts promptly respond, enabling stable and efficient operations 24/7. This significantly enhances the logistics efficiency of the enterprise.

2. Improved storage space utilization: When the autonomous forklift (VNP20) retrieves and stores the stacks of finished products, its high-precision sensing and positioning methods, combined with servo control technology, enable precise stacking in three tiers. This effectively enhances the client's storage space utilization rate.

3. Flexible response to human-robot collaboration: The project site covers a large area with frequent movement of personnel. The VNP20 autonomous forklift is equipped with 360° laser obstacle avoidance, providing comprehensive and three-dimensional protection. This allows it to flexibly navigate and adapt to complex environments involving human-robot collaboration.